Cross Selling & Upselling: Everything You Need to Know!

What happens when you’ve got five different items and want to sell them all? You could run five different ads to sell them all individually…or you could do something called upselling & cross selling.
Now, you might be thinking to yourself that this is a wonderful idea if you don’t have to spend more on ads and marketing.
The only problem is that you don’t know what either upselling or cross selling is.
In our article today, we’ll be looking at what they are, why they are important, what you can upsell or cross-sell, how to do so effectively, and whether you should do so.
What are Cross Selling and Upselling?
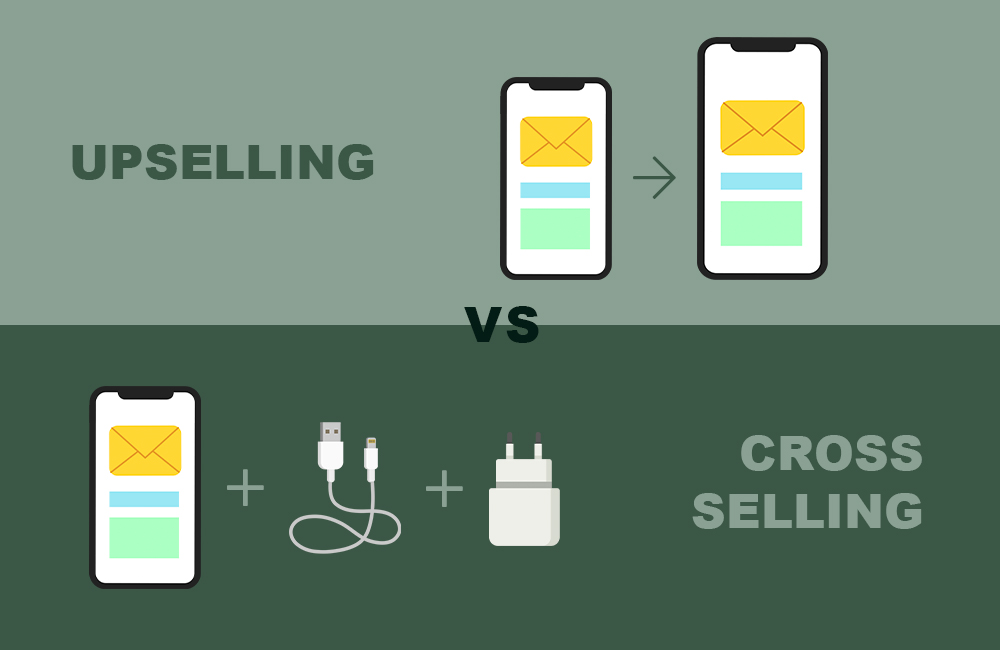
We start with the first thing that we’ll need to understand things - definitions.
Upselling is when you sell something more expensive than what the customer originally wants to buy, hence why it’s up.
Cross selling is when you sell something supplementary to the original item that the customer wants.
Here are two examples to give some details of them both.
If you are looking to buy a phone from me for $1000, you can get a nicer one for $150 more: the better phone is an upsell.
If you buy a phone from me, I'll throw in a pair of USB-C earphones for $25 as a bonus: the pair of earphones is a cross-sell.
From the example, we can see that Upselling is a sales tactic that involves selling a better, more expensive version of a product that the client already possesses (or is buying) whereas Cross selling is a tactic for selling products that are similar to those that a consumer already possesses (or is buying).
However, there is a method wherein you combine both of them and you get something that’s called Bundling.
What is Bundling?

Bundling is when you sell two or more things together as a package which usually adds up to being a more affordable alternative to getting the individual items separately. We see this done everywhere these days from set lunches of drink and food to handphones that come with an included phone case or even a camera with a memory card bundled in the package to sweeten the deal.
Bundling is frequently used in conjunction with a discount to boost the perceived value of the offering.
Pure bundling occurs when products are only offered in bundles and cannot be purchased separately. When both alternatives (individual buy and bundle buy) are made available, this is referred to as mixed bundling.
According to a study on bundling as done by Nintendo in their video game market, revenues plummeted about 20% when Nintendo went from mixed bundling to pure bundling. Customers wishing to buy a single item in the gaming industry will choose to wait till it becomes available, most likely at a lower price.
The question now is if you should employ upselling, cross selling, straight bundling, or mixed bundles. However, let’s first recap with the following table:
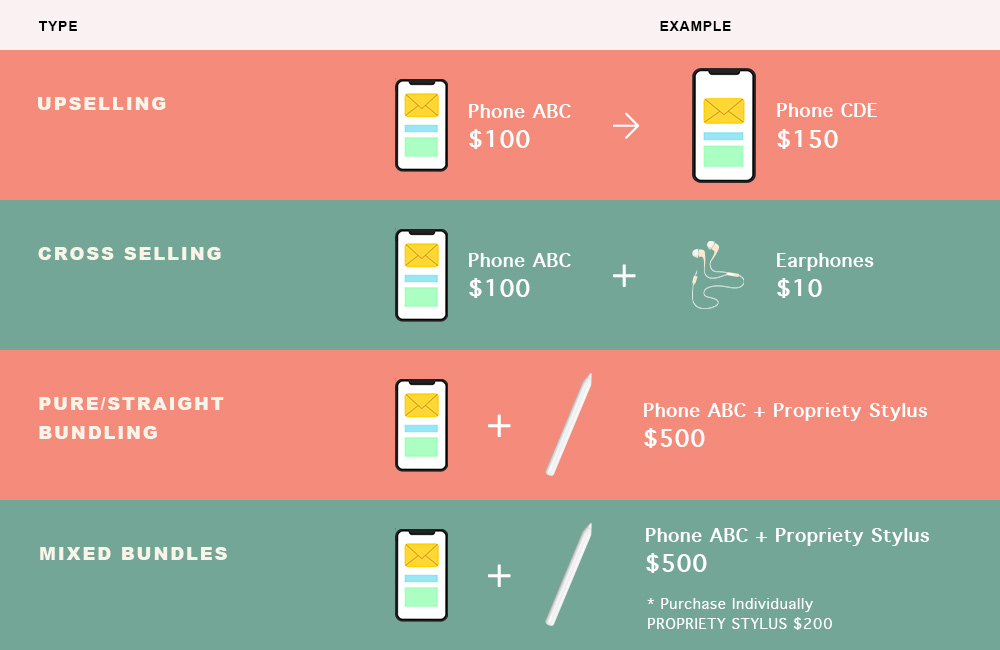
The simple answer to decide which of these will work best for you is - A/B test and keep track of the data to find out which methods work best for you!
Why are They Important?
Upselling and cross selling are frequently and incorrectly viewed as underhanded practices that are used to extract more money from customers.
However, as a strategy, upselling and cross selling should be employed to 'help clients win.' It is about giving recommendations that may better satisfy a customer's present needs and assisting them in making an informed decision about their options.
Think about it this way, if you buy a scented candle, how would you use and enjoy it when you don’t have a lighter to light the candle? Hence you’ll need to buy a lighter IN ADDITION to the candles (cross selling).
Another way to look at it is if your customer is getting a laptop that’s $4500, but you being the tech-savvy salesperson that you manage to argue the point that if they spend $4500 now, should new processors or graphics cards come out, they would have to spend a FURTHER $4500 in the future to upgrade their system. However, if they spent an extra $500 for a PC, they’ll have a system that they can upgrade for much lower than $4500 in the future (upselling).
Benefits?
Here are some benefits of cross selling and upselling:
• Enhances Client Retention
Aside from impulse purchases, individuals purchase products and services to solve an issue. They are aware of the problem, but may not be aware of the appropriate remedy.
When Steve Jobs said, "people don't know what they want until you show it to them," he was correct. When upselling or cross selling is done well, the customer receives more value than they expected. It has the potential to raise sales by up to 43% while also improving client retention.
• Increases The Average Order Value & Lifetime Value Of A Customer.
Cross selling and upselling boost your average order value, resulting in increased revenue and profit at a low incremental cost. You've already invested money in marketing to attract the buyer to your eCommerce store, so increasing order value is critical to ROI.
According to a Marketing Metrics study, the likelihood of selling to an existing customer is 60-70%. The likelihood of selling to a fresh prospect is 5-20%. Upselling to existing clients is a low-cost strategy to increase lifetime value.
Deciding What & How You Should Upsell/Cross-sell

One of the most prevalent methods of upselling is to recommend the next higher model. However, when the target is only 4%, the margin for error is as tiny as the edge of a knife.
Here are some ideas for upselling:
✣ Promote your best-reviewed or best-selling products.
✣ Increase the prominence of the upsell and display testimonials for the upsell.
✣ Use client personas to provide relevant ideas if you have them.
✣ Make suggestions more relevant by providing context: why should I buy that rather than this?
Make sure you only recommend products from the same category. When a website visitor is looking for a pair of hiking boots, don't ask them to buy a laptop or even a pair of running shoes. The two latter goods do not match the same demands.
Cross-sell extra on the checkout page to capitalise on impulse purchases:
✣ Cross-sell products should be at least 60% cheaper than the product added to the cart so that shoppers consider adding them to their carts even if they did not intend to buy them.
✣ Look for things that are easily overlooked, such as lens filters, headphones for mobile phones, lighters for gas stoves, and, of course, cow scrub... the possibilities are unlimited.
✣ Try not to overwhelm them with options that will distract them and cause them to abandon their cart.
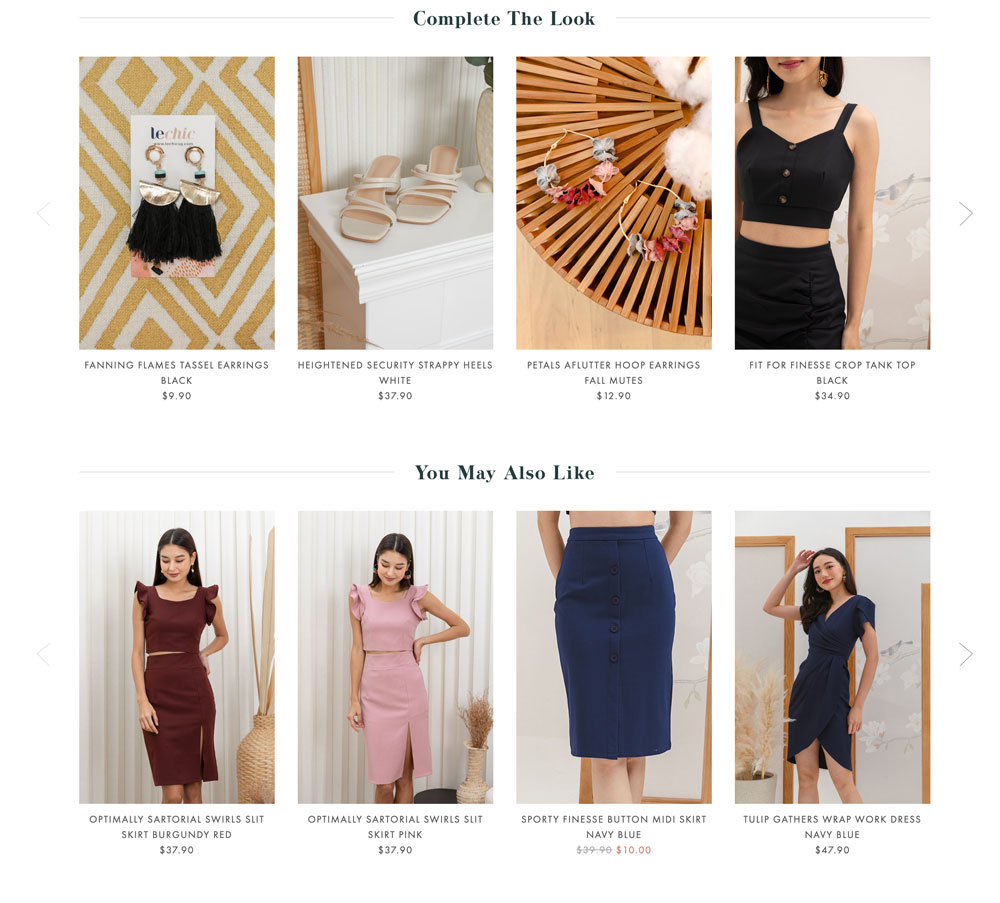
It would be good to automate the method if you are manually pushing upsell/cross-sell suggestions. To enable automation, products should be categorised and similar products should be tagged as seen in the example below.
How to Effectively Carry It Out?
Upsell and cross-sell work best when you can help a customer make a decision.
According to a Bain study, lowering complexity and narrowing options can increase revenues by 5-40% while decreasing costs by 10-35%.
✧ Be Smart By Narrowing Options
Too many options can be overwhelming. Professor Iyengar and her research assistants studied the impact of options in the California Gourmet market. They set up two Wilkin and Sons Jams booths, one with a selection of 24 jams and the other with six jam kinds on display.
60% of visitors stopped by the larger booth, whereas only 40% went to the one with fewer options.
However, 30% of visitors who sampled at the tiny booth made a purchase, whereas only 3% of the 60% who visited the larger stand made a purchase.
Also, keep in mind not to overwhelm your clients with options. Do not press for an upsell product if they have already said no. Consider upselling to be a friendly suggestion rather than an aggressive sales strategy. And, when in doubt, run an A/B test!
✧ Bundle to Lessen Choice Paralysis
Every action the user must take complicates the decision-making process. Consider approaches to reduce the number of steps in a purchasing decision. We have a finite amount of energy to devote to decision-making.
Bundling combines related products that are relevant to a buyer. Purchasing them separately necessitates extra decision-making and procedures. Whereas by bundling, a buyer can purchase many things at the same time.

✧ Utilise Price Anchoring: The Surprising Power of Dummy Options
You can acquire a web-only subscription for $59, a print-only subscription for $125, or both for the same price! Needless to say, the print-only option is a non-starter. When the price is the same, who would choose the poorer option?
Dan Ariely took the advertisement and distributed it to 100 MIT students to see what people would choose.
The overwhelming majority chose what appeared to be the 'best' option - a $125 print and web subscription.
The web-only subscription was chosen by 16% of those polled. Nobody picked the $125 print-only subscription.
Dan then removed the middle option—the print-only option. And then repeated the experiment on 100 people. This is how the opt-in rates appeared right now.
Surprisingly, when the dummy option was removed, the majority (68%) of participants chose the cheaper option. The print and web subscriptions, which had an 84% subscription rate in the absence of the dummy option, now have a substantially lower 32% subscription rate.
Even if other options are cheaper, an inferior choice makes a similar but superior one appear better.
Consider a consumer who is considering purchasing a top-tier entry-level handphone. Show him a mid-level handphone without added accessories for a marginally higher price, and the same mid-level handphone with added accessories for the same marginally higher price.
Upselling with a solid pitch and think how this mid-level handphone helps the customer benefit. Incorporate that and you’ll have a good chance of making the upsell.

✧ Be Helpful Rather Than Forceful or Confrontational.
One of the most important principles in cross selling and upselling is to aid the consumer by offering goods that make sense to them and are relevant to their needs. Make knowledgeable recommendations based on data and customer behaviour that are likely to suit their wants or solve a current or potential problem.
Here's what you should avoid:
• Before a customer chooses a product, suggest upsells and cross-sells.
• Customers should not be bombarded with too many cross-sell and upsell products.
• Sly techniques such as concealing pre-selected add-ons in the expectation that clients will not find out.
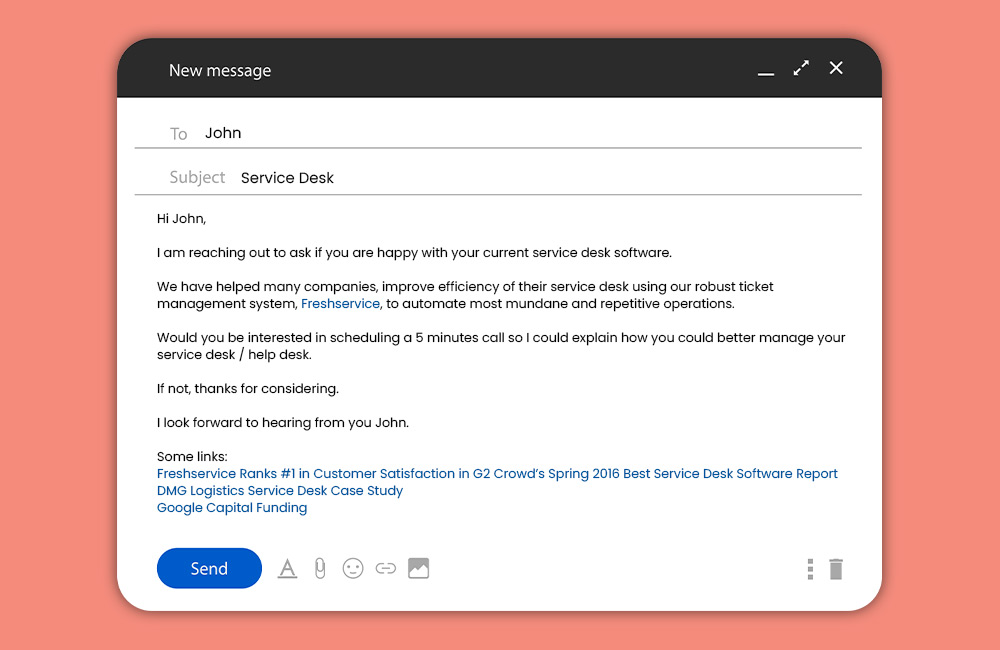
✧ After Purchase Cross Selling
Once the customer has checked out, your chance to cross-sell does not disappear. Indeed, the experience after the purchase is a critical stage in the customer journey that far too many eCommerce businesses overlook. Don't just deliver the receipt and the merchandise; instead, take advantage of the opportunity to build loyalty and make special offers.
You can use emails, confirmation pages, and other post-purchase communications to give the customer additional items, incentives, and value. This can be seen in the example below:
Closing Words
If you just remember one item from this post, make it this:
Upsell and cross-sell approaches are effective strategies for assisting clients in making better selections faster.
You shouldn't rely on guessing to find out which of these will work for your customers. A/B test various upsell and cross-sell techniques for your various visitor segments to identify what works best for each of them, so you can apply the one that results in the greatest increase in sales.

